Trying to Get Pregnant
For most couples trying to have a baby, the chances of achieving a pregnancy are 60% after 4 months, 75% after 6 months, and 90% after 1 year of trying.
There may be a subfertility issue if a couple fails to get pregnant after 1-2 years of trying.
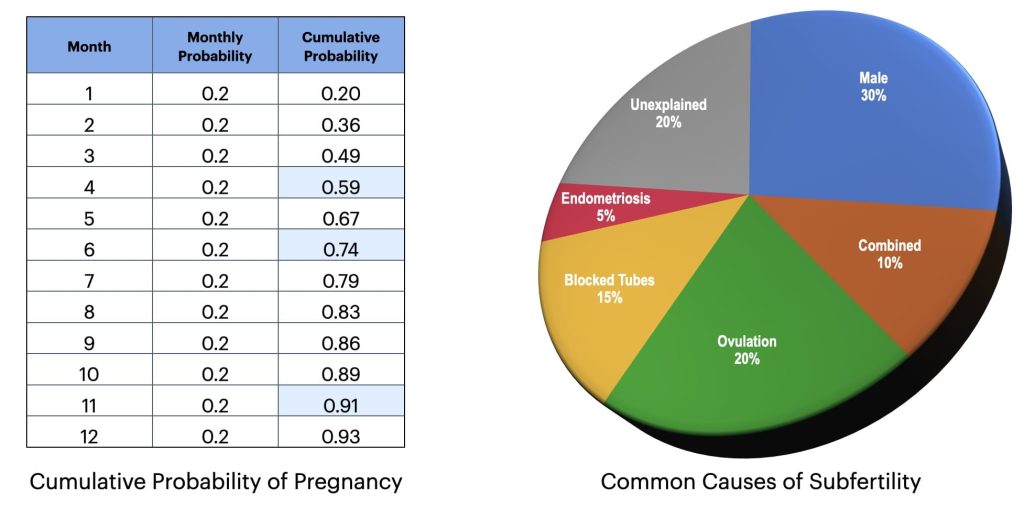
Subfertility affects 10-15% of couples.
In 30% of cases, a male factor is found, while in 40% of cases, a female factor is contributory. In some 20% of cases, the reason for subfertility remains unexplained.
Couples Who Can't Get Pregnant After One Year
It is advisable to see a gynaecologist if you can't get pregnant after trying for one year.
If you are 35 years or older or have irregular and painful menstrual cycles, you should see a gynaecologist earlier.
Subfertility Investigations
Ovulation Testing
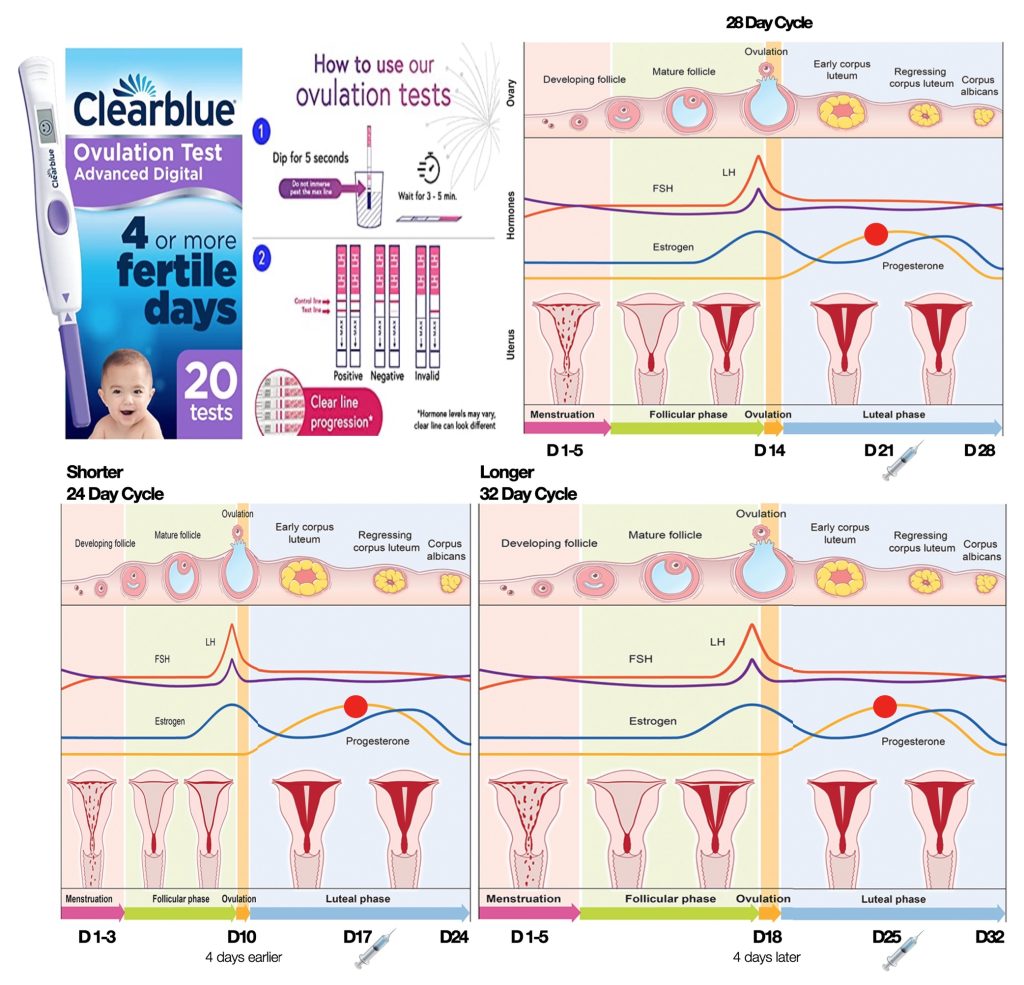
❖ Urine Ovulation Test Kits, checking 2-3 days before ovulation.
❖ Blood Progesterone level (>30nmol/L), taken 7 days after ovulation, confirms ovulation.
Tubal Patency Testing
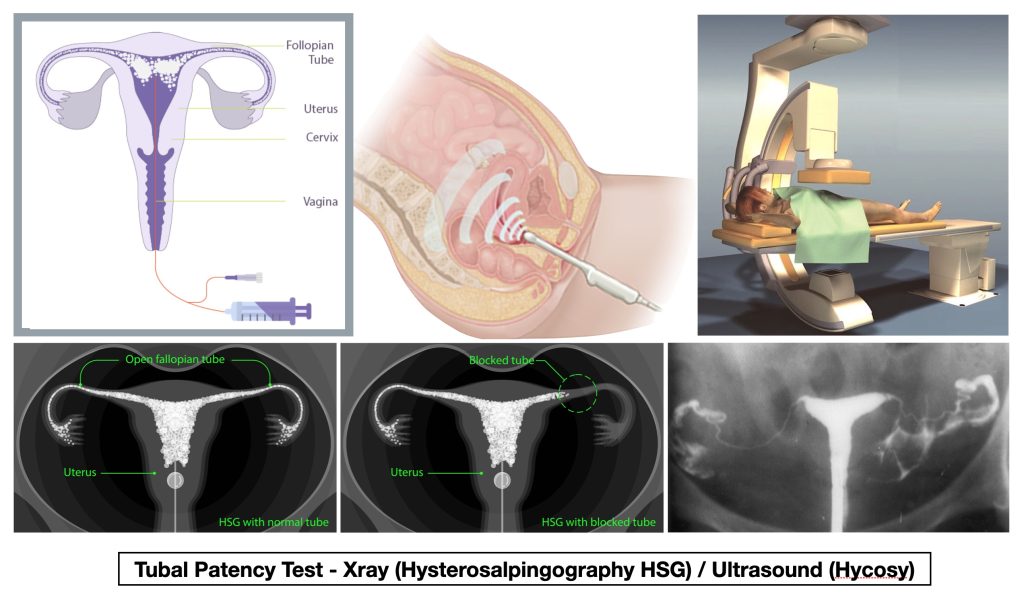
❖ Checking that the fallopian tubes are not blocked by Ultrasound or X-ray.
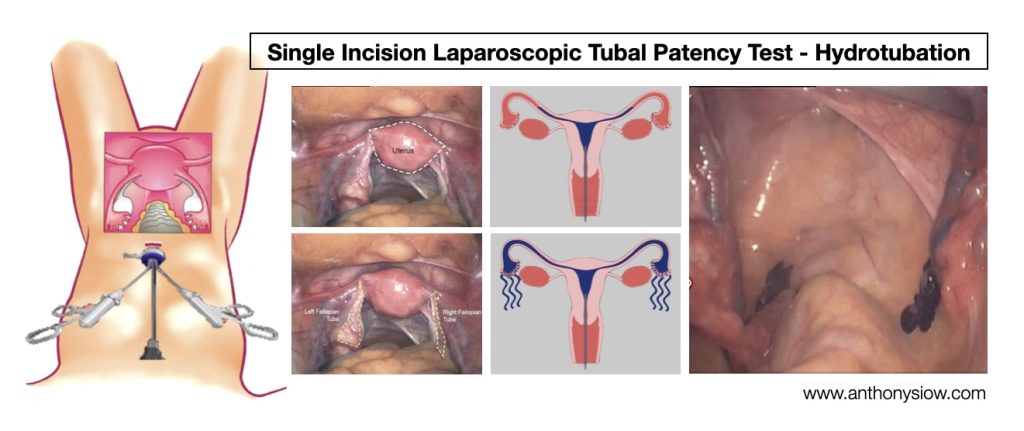
❖ Checking that the fallopian tubes are not blocked AND looking for other causes of subfertility (eg. Endometriosis, Pelvic Adhesions) by Single Incision Laparoscopic Keyhole Surgery. This is a day surgery procedure that has the added benefit of surgically treating conditions to improve fertility.
Sperm Analysis Testing
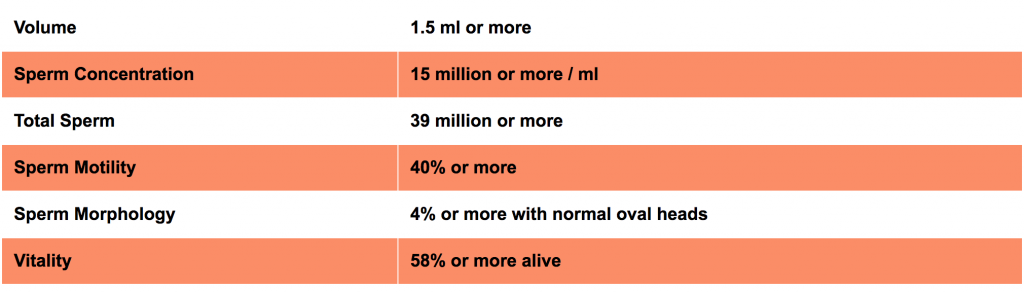
Total Sperm Count and Sperm Motility are more important factors than Sperm Morphology.
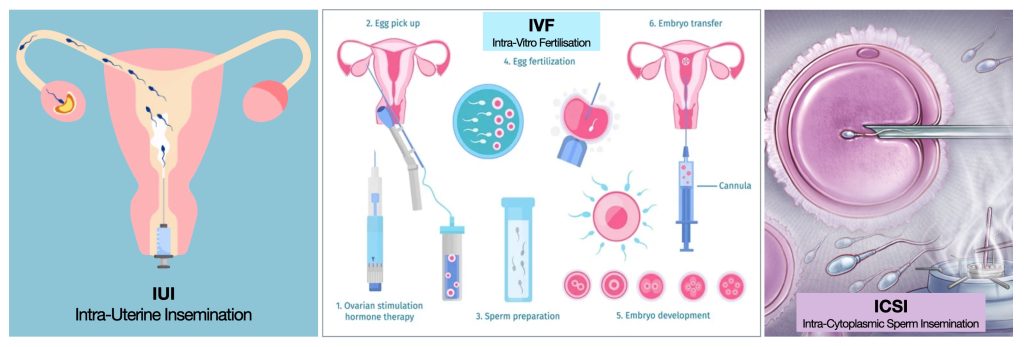
At least 20 million sperms with 50% motility are needed for the Intra-Uterine Insemination procedure.
Facts in Trying to Get Pregnant
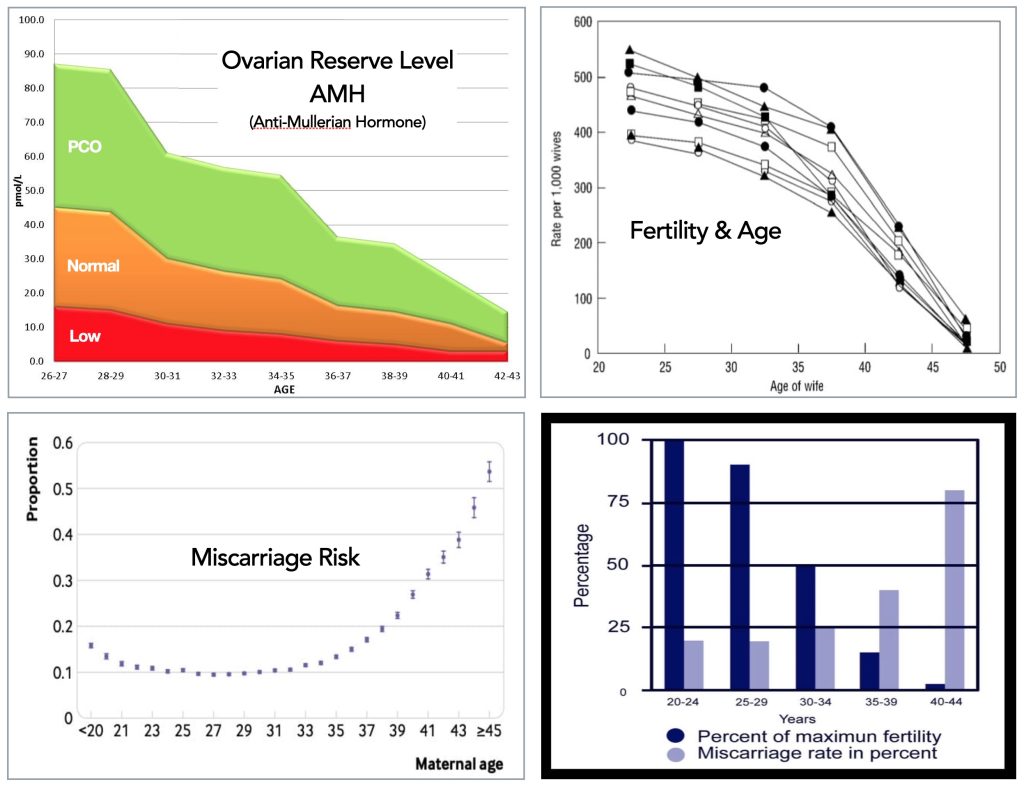
❖ Age of the woman is an important consideration. The chance of pregnancy drops after age 37 and there is an associated increased risk of miscarriage.
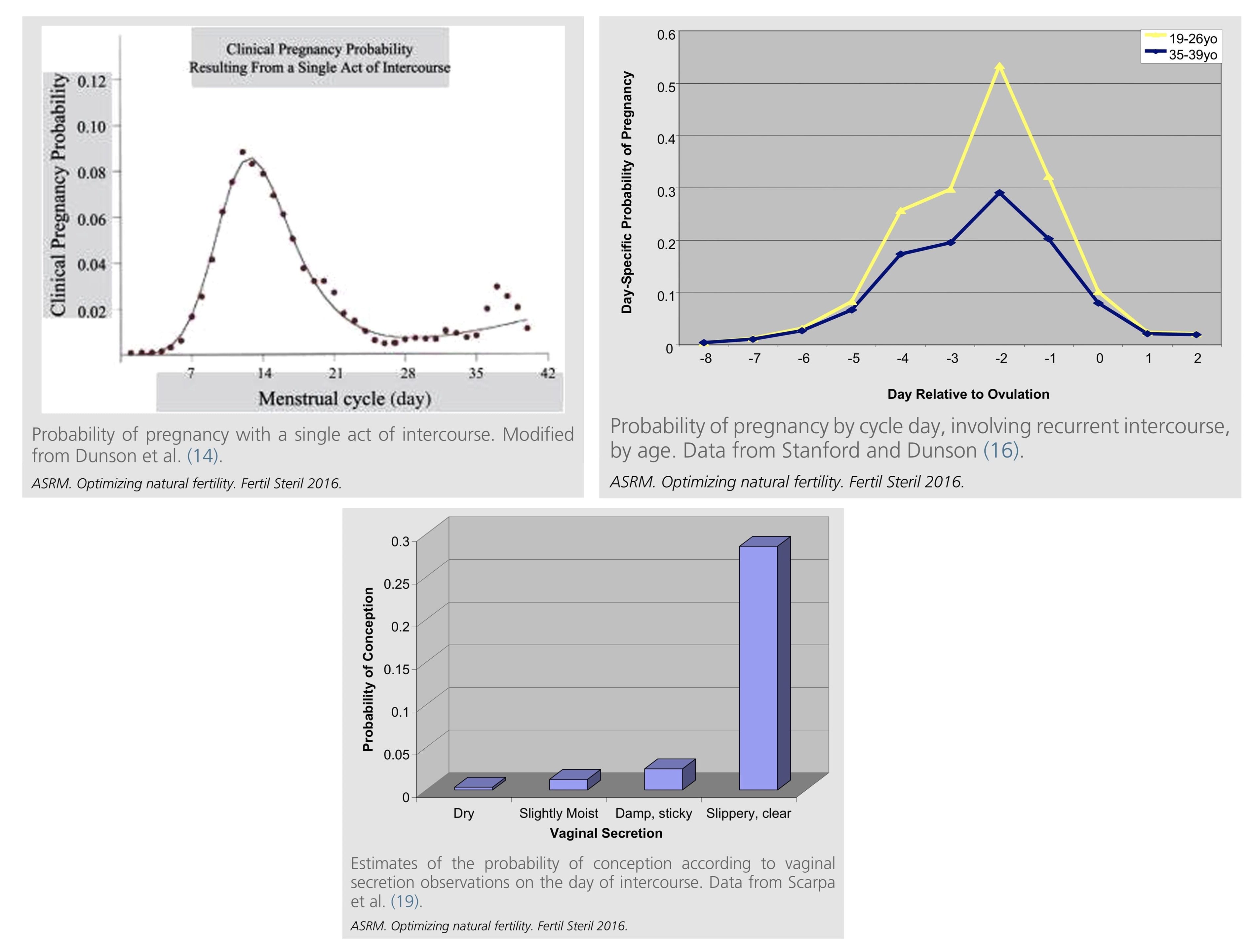
❖ Frequency of intercourse. 37% got pregnant from daily intercourse, 33% from every other day, and 15% from once a week. This was the result of 221 fertile couples planning to conceive (Wilcox NEJM 1995).
❖ Timing of intercourse. Pregnancy was highest with intercourse beginning 2 days before ovulation. The chances of pregnancy from one act of intercourse are 3.4% at 4 days before ovulation, 9.4% at 2 days before ovulation, and 8.0% on ovulation day itself.
❖ Vaginal Secretion. The probability of pregnancy was highest when the vaginal secretion was slippery and clear. This usually occurs 2 days before ovulation (Scarpa EuJOGRepBio 2006).
❖ Temperature & Urine Ovulation Kit. Measuring basal body temperature and using Ovulation Kit is good. However, studies show that vaginal secretion is a better gauge. This was the result of 782 couples planning to conceive (Bigelow HumRepro 2004).
Diet and Lifestyle for Pregnancy
❖ Keep a BMI between 20 and 30.
❖ Start exercising.
❖ Start taking folic acid 400 mcg daily.
❖ Stop smoking and reduce alcohol intake. Smoking reduces pregnancy by 60%, and Alcohol of >2 drinks/day reduces pregnancy by 45%.
❖ Caffeine of 1-2 cups a day has no impact on pregnancy. Caffeine of >5 cups a day can reduce pregnancy by 45%.
❖ Take 2 or more servings of seafood a week to increase your pregnancy chances. This was seen in 501 couples in the LIFE Study (Longitudinal Investigation of Fertility & Environment). Couples taking seafood had a 61% higher chance of pregnancy. It is thought that the omega-3 in fish and shellfish improves sperm quality, ovulation function and embryo development (Gaskins JClinEndoMetab 2018).
Treatment for Subfertility
❖ Oral Medication (Clomid / Letrozole) or Fertility Injections to improve Ovulation
❖ Surgery to remove Ovarian Cysts or Restore Tubal Function.
❖ Supplements (Profertil) and a healthy diet to improve sperm quality.
❖ Intra-Uterine Sperm Insemination or Assisted Reproductive Techniques like IVF and ICSI may be required for some couples.