Fibroids
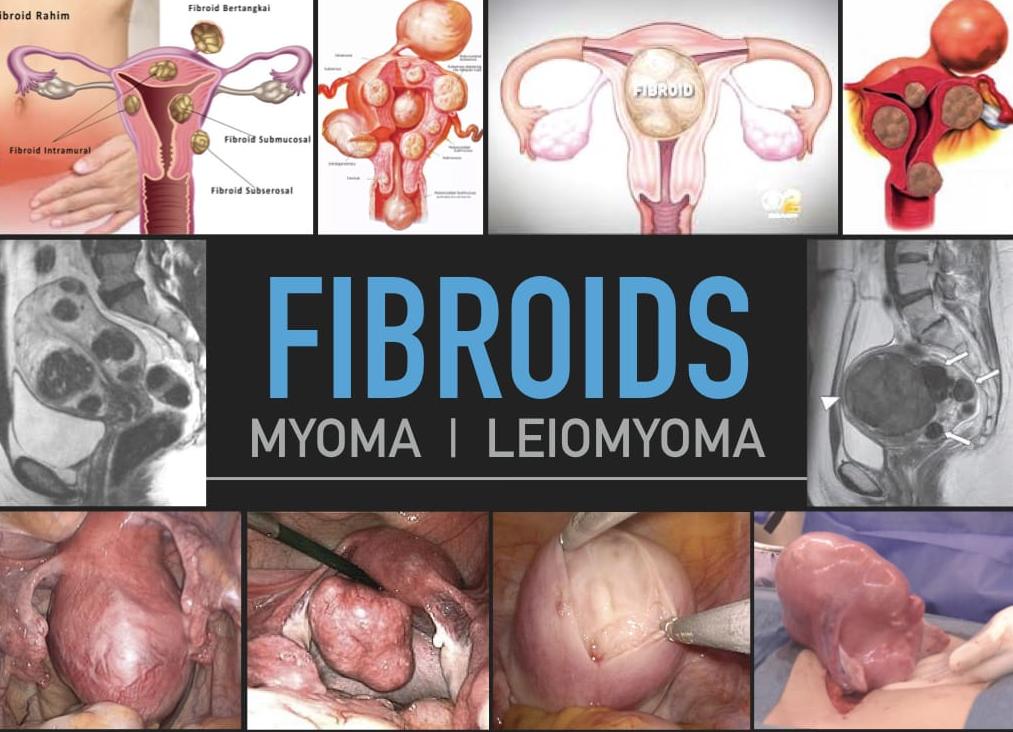
Fibroids are lumps of muscle, like meatballs, growing within the womb.
Studies have found that 75% of women attending health screening can have fibroids detected on pelvic ultrasound. Fortunately, more than 50% of these fibroids do not need treatment.
More than 99% of fibroids are benign and do not become cancers.
The exact cause of fibroid is unknown. Some studies suggest growth factors and blood flow changes within the womb as contributing roles. A family history of fibroid increases your chance of having fibroid whereas pregnancy reduces the chance.
Surgery (called Myomectomy) is the mainstay of treatment for problematic fibroids.
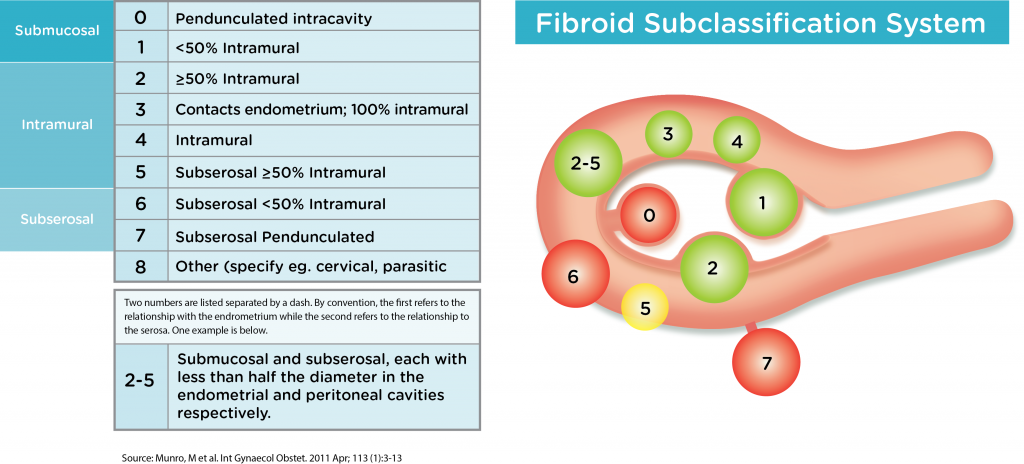
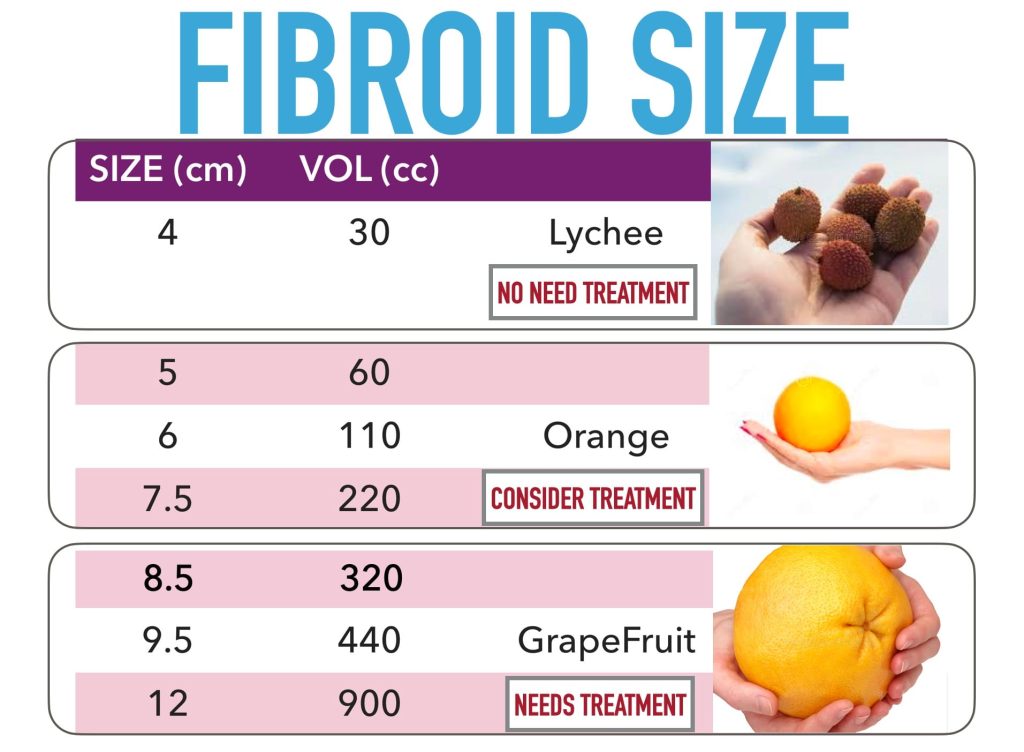
Most Fibroids smaller than 4cm have No Symptoms
Some Fibroids can have the following Symptoms
❖ Heavy menstruation is the most common symptom
❖ Pressure on the bladder causing frequent urination or urinary blockage
❖ Pressure on rectum & lower back from larger fibroids
❖ Pain from fibroid degeneration
❖ Subfertility and pregnancy-related issues
Small fibroids (1-3cm) Not Causing Symptoms DO NOT NEED Treatment
What is the Natural History of Fibroids
The usual behaviour of fibroids is that they grow in size with age until menopause, when they start to shrink.
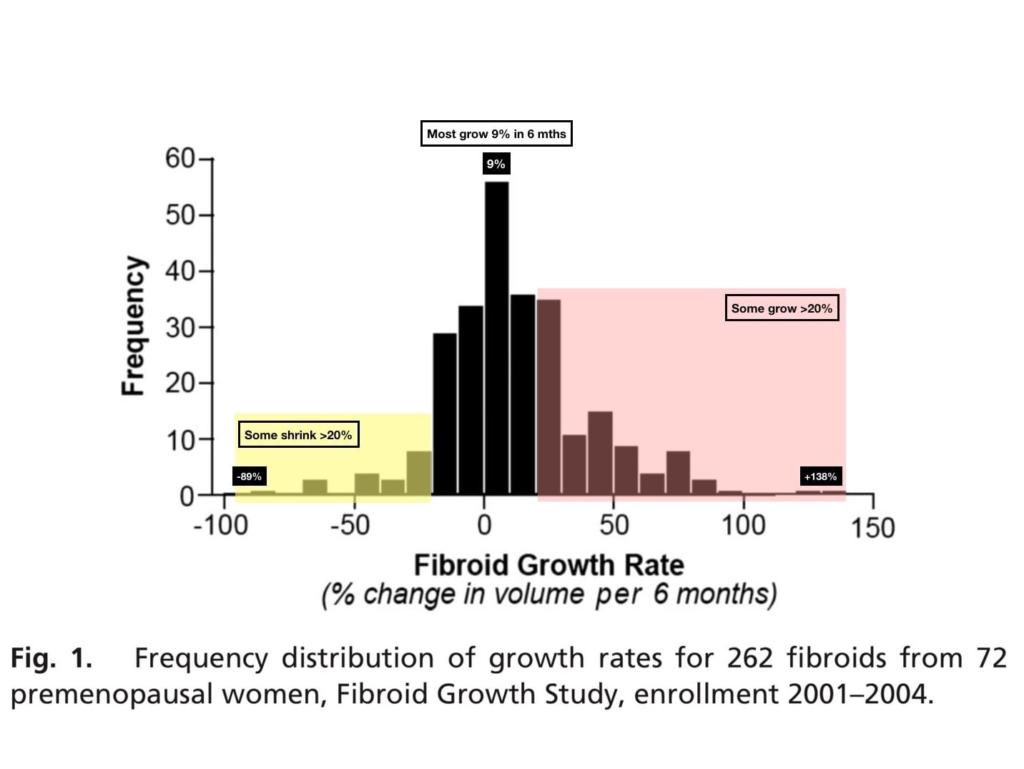
From the Fibroid Growth Study, looking at 262 fibroids in 72 women, it was found that most fibroid grow at the rate of 9% every 6 months.
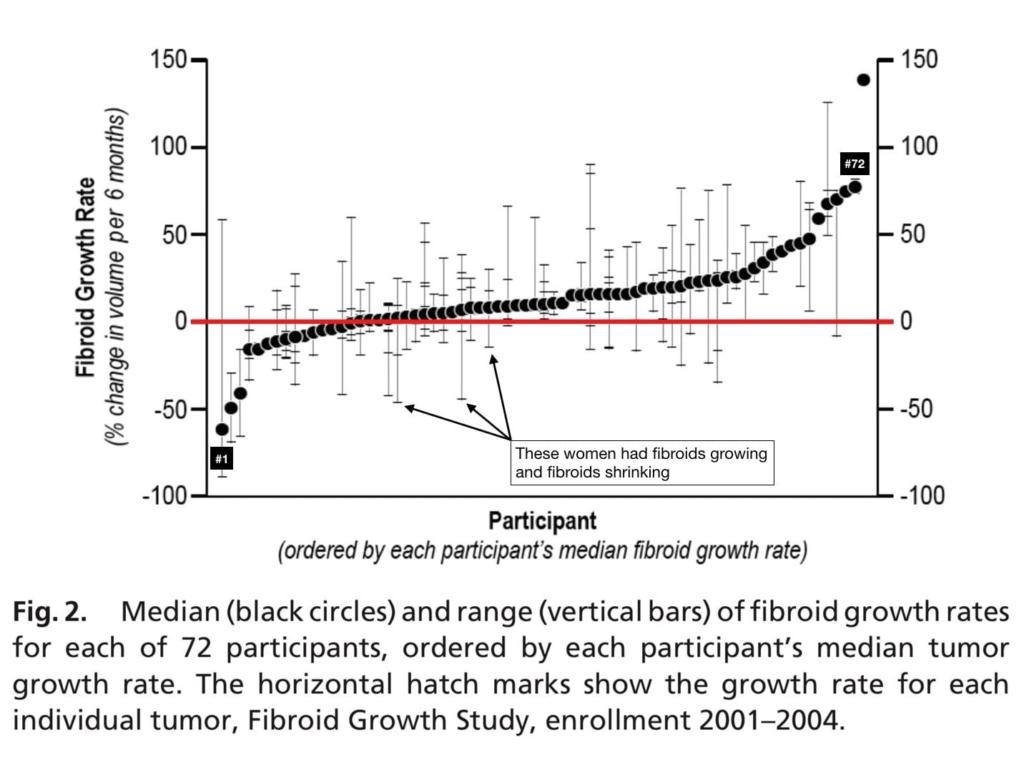
It was also found that, some fibroids within the same woman can grow at different rates, while other fibroids may shrink at the same time.
Can Fibroids become Cancerous?
From large studies, it was found that the chance of finding cancer within a fibroid is around 1 in 2000-8300. (Pritts 2015).
Professor William Parker, a renowned expert on fibroids also found that rapidly growing fibroid is not a sign of cancer. (Parker 1994)
You can get more information on fibroid and cancer at www.fibroid.com.
When do fibroids need treatment?
Treatment is needed when fibroids are
❖ large (6-8cm or larger) or growing rapidly
❖ causing symptoms like heavy menstruation, pain or pressure sensation
❖ contributing problems to fertility and pregnancy.
Medical Treatment for Fibroids
❖ For Bleeding - Tranexemic Acid and Menopausal Injection (GnRH) are effective. Birth control pills, birth control injections (DepoProvera) or hormonal implants (Mirena) may also be helpful. However such hormones may encourage some fibroids to grow while stopping the bleeding problem.
❖ For Pain - Panadol, Ponstan, Synflex, Nurofen, Arcoxia, Tramadol.
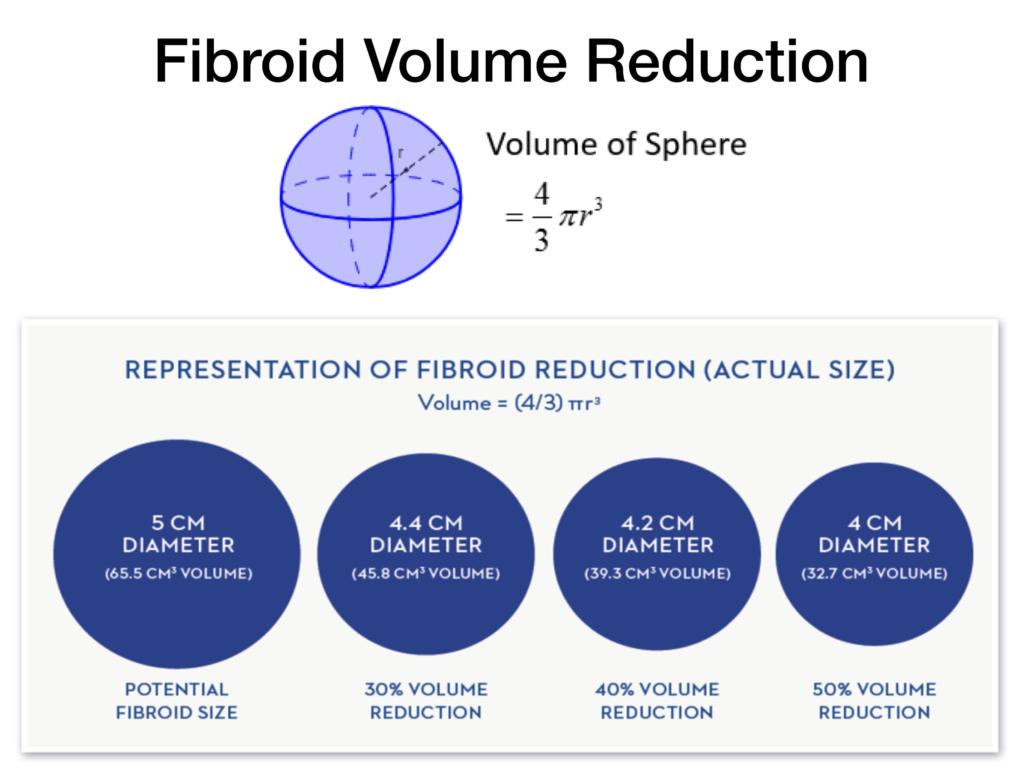
❖ For Size Reduction - Menopause Injection (GnRH) can shrink the fibroids. However, the fibroid will grow back in size after treatment. Hence GnRH injections are mainly used to shrink fibroids in preparation for surgery.
Ulipristal (Esmya) is an oral tablet taken daily for at least 3 months. It is very effective in reducing heavy bleeding caused by fibroids. It also shrinks fibroids over 3-6 months of treatment.
However in Sept 2020, the European Medicines Agency revoked the use of this medication because of the rare (<0.1%) but unpredictable risk of liver injury associated with its use.
Non Surgical Treatment for Fibroids
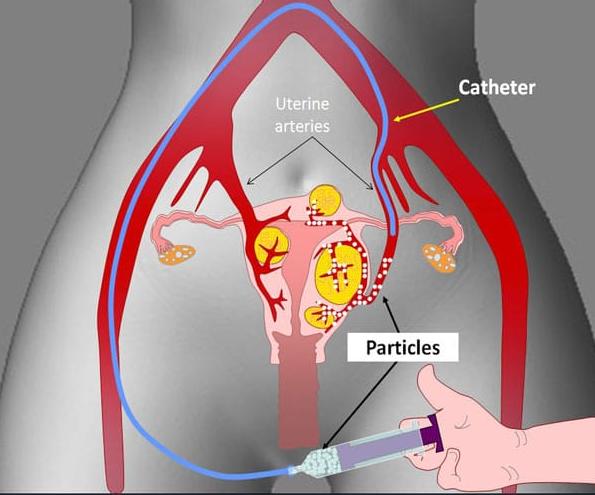
❖ Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE) - a procedure to block the blood supply of the womb and fibroids
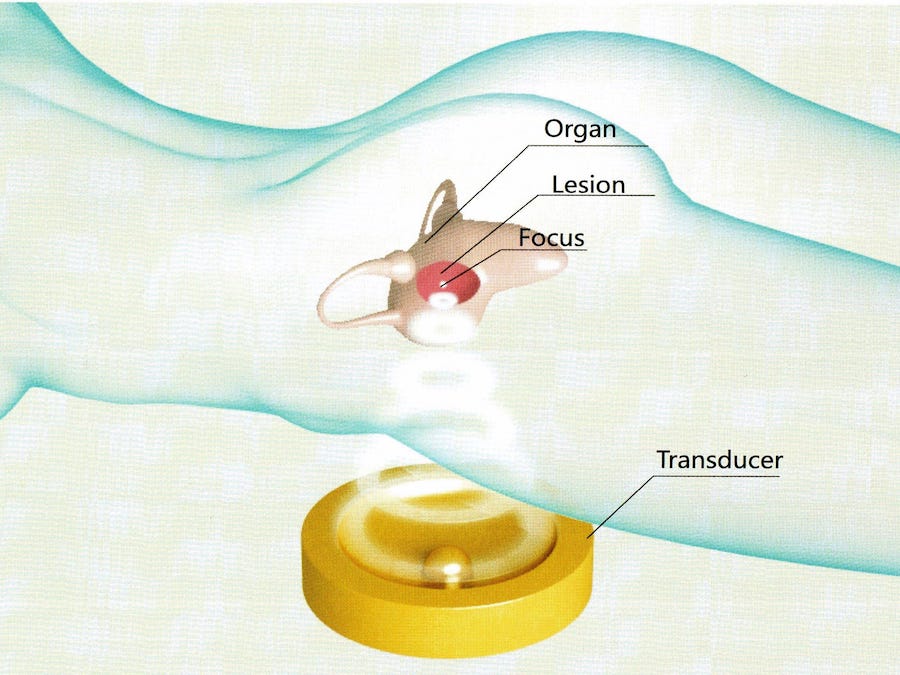
❖ High-Intensity Focus Ultrasound (HIFU) - a procedure to ablate or burn the fibroid with a strong ultrasound beam
❖ These treatments are effective in reducing heavy bleeding caused by fibroids. They also shrink the fibroid size by 1-2cm over 6-12 months.
Surgical Treatment for Fibroids
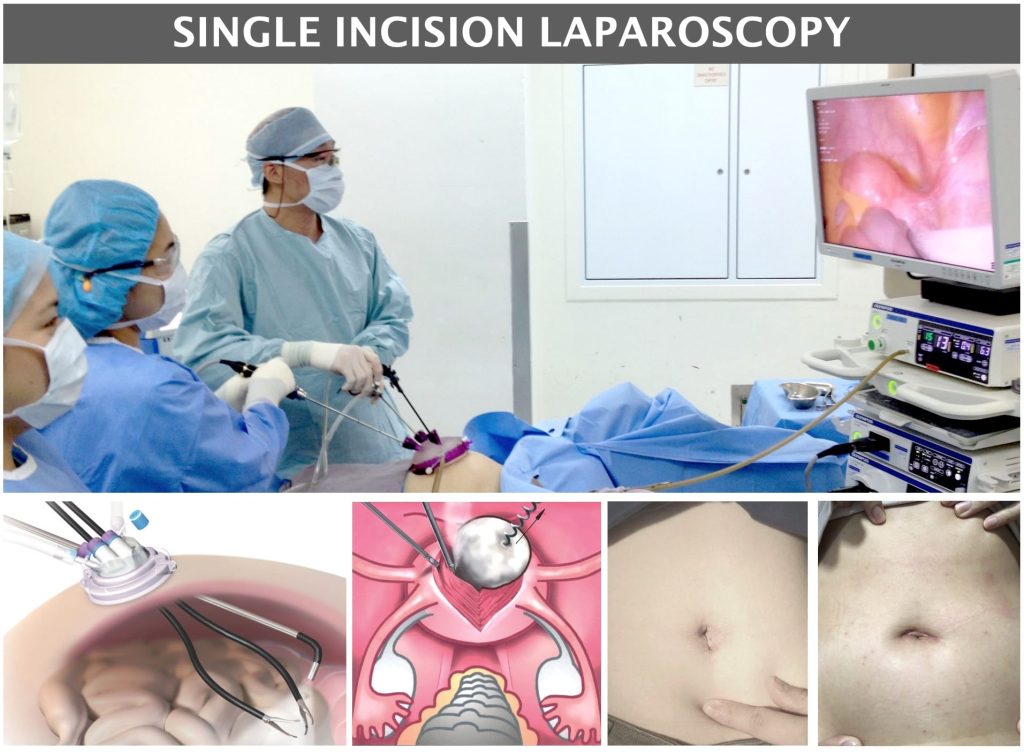
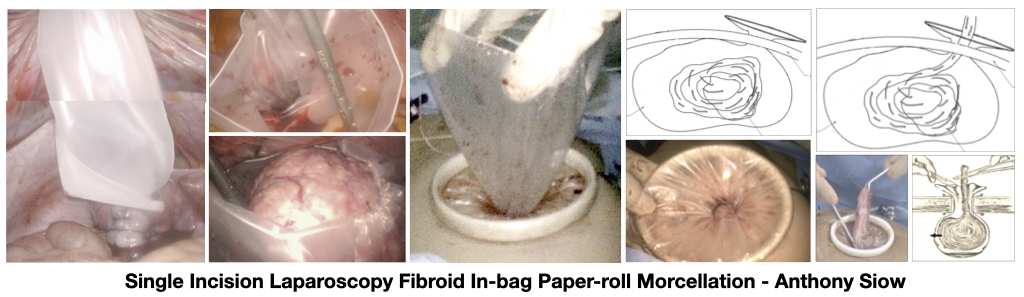
Single Incision Laparoscopy is done with Just One Cut of 3cm at the belly button.
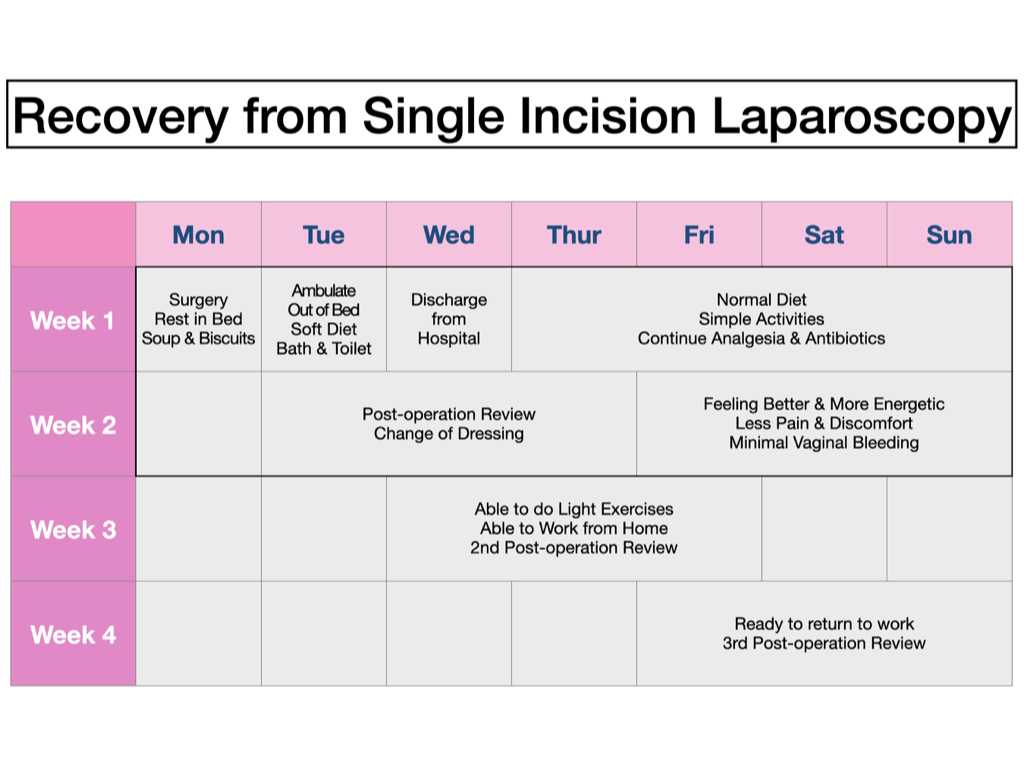
This is a more advanced laparoscopy surgery that has the benefits of a fast recovery and a surgical scar that is barely visible.
Anthony Siow first started Single Incision Laparoscopy in 2009. He now carries out more than 90% of his fibroid surgery through this method with Just One Cut.
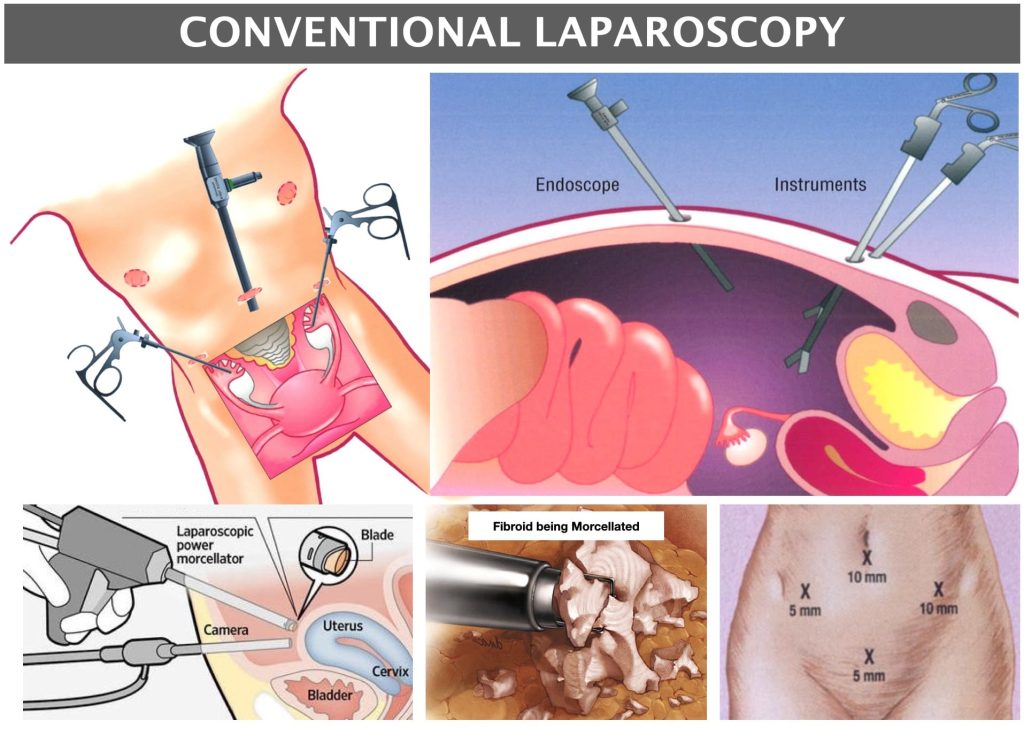
Conventional Laparoscopy is done with 3-4 small abdominal cuts of 0.5 to 1 cm.
It also has a fast recovery but requires the use of the Power Morcellator.
Power Morcellator used without a containment bag is now discouraged because of the possibility of the spread of fibroid bits within the abdomen.
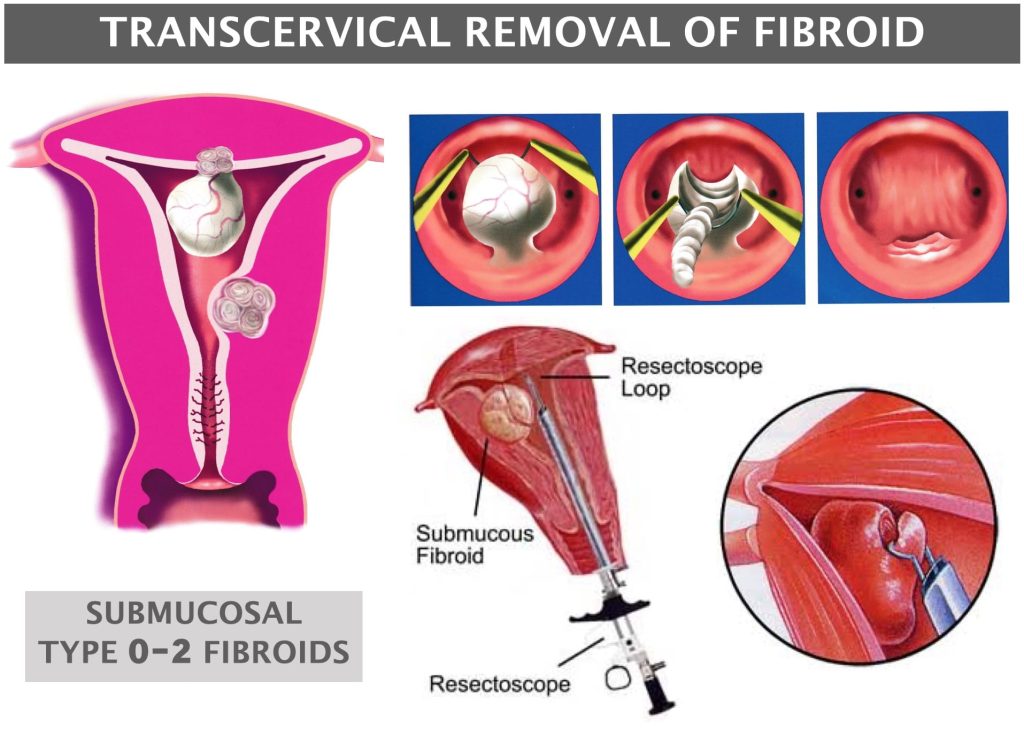
Transcervical Removal of Fibroid (also called Transcervical Resection of Myoma TCRM) is a special surgery for fibroids found inside the womb cavity.
It is surgery done through the vaginal and cervix and requires advanced surgical dexterity and special instrument (called Resectoscope) to perform.
Recovery is within 1-2 days and heavy menstruation from submucosal fibroids is effectively treated.
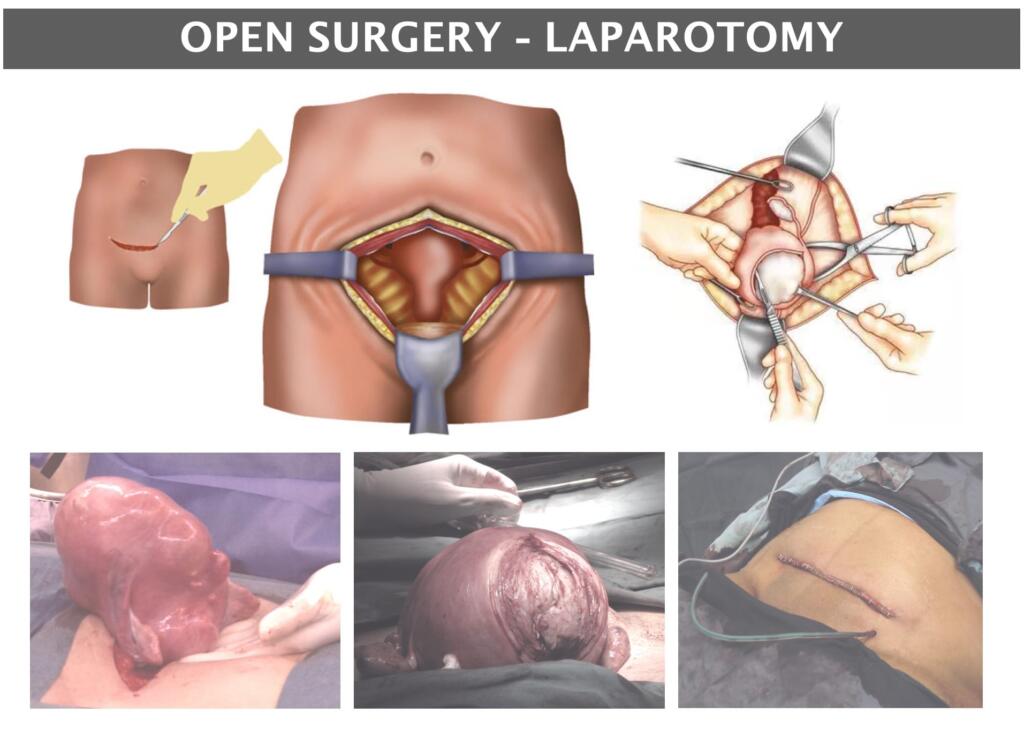
Open Surgery or Laparotomy is done with an abdominal cut of 10cm or more.
It is a good procedure for the complete removal of all fibroids, both small and large. It is also the preferred procedure for very large fibroids.
As with all open surgery, recovery can take between 2-4 weeks or longer.
You can get more information and Facts on Fibroids at
www.fibroid.com.sg
