Polyps
What are Polyps & Why do they form?
Polyps are like skin tags and extra folds overlying skin or lining.
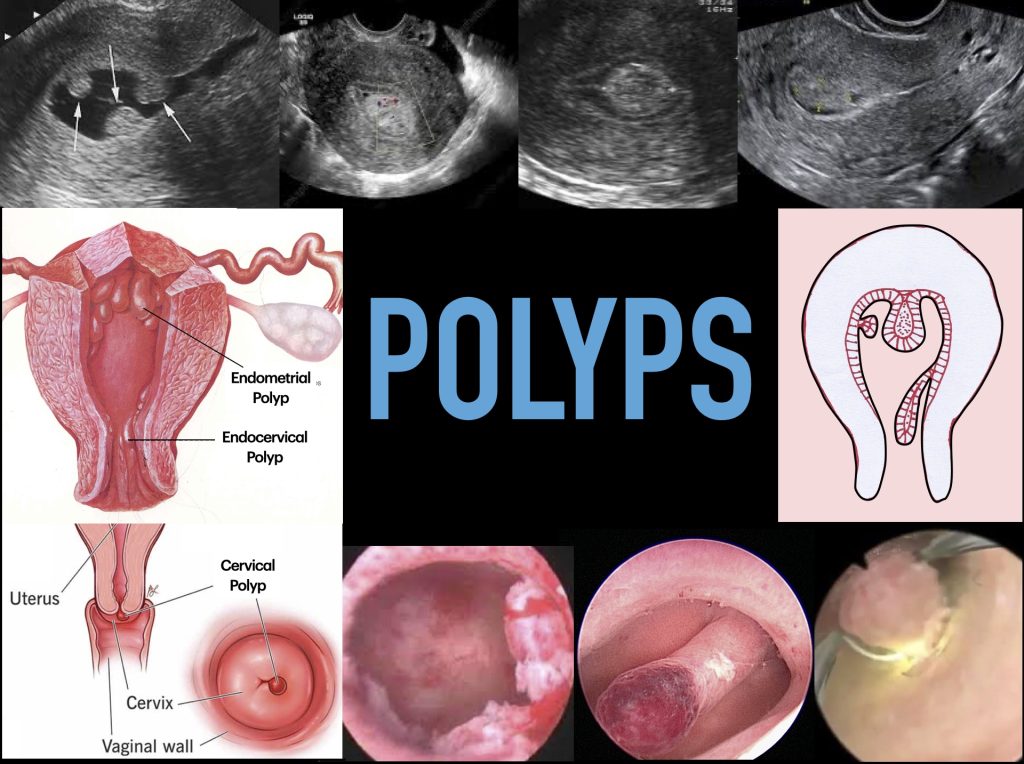
Endometrial Polyps are overgrowths of the endometrial lining inside the womb.
Cervix Polyps are overgrowths of the cervix lining at the endocervix or external cervix.
The cause of Polyps is unknown. Hormonal imbalance and genetic factors (like abnormalities of chromosomes 6 and 12) may be the cause. (Vanni et al). An increase in p63 proteins which encourage the basal cell activity of the endometrium has also been reported. (Norgueira et al)
Who is likely to have Polyps?
Polyps can be found in 8-35% of women depending on the population surveyed and the diagnostic test used.
Older women who are obese are likely to have Polyps. It seems to occur more in postmenopausal women (12%) than premenopausal women (6%). Women with hypertension are also more likely to have Polyps.
Women taking Tamoxifen for breast cancer treatment are more prone to form Polyps.
Women taking the birth control pill have a lower risk of Polyps (2% vs 6%). (Dreisler et al)
What are the common symptoms of Polyp?
❖ abnormal and irregular vaginal bleeding
❖ pre and post-menstrual spotting
❖ bleeding at sex and after exercises
❖ subfertility possibly from the Polyp blocking the fallopian tube entrances. Studies have shown higher pregnancy rates after Polyp removal. (Lieng et al)
30% of women with Polyps have no symptoms; their Polyps are found on health screening.
Symptoms do not seem to correlate with Polyp number, size or site. (Hassa et al)
What happens to a Polyp? Can it become Cancer? How is it removed?
Up to 27% of Polyps can disappear after 1 year. Those that disappear tend to be smaller Polyps (<10mm) (Lieng et al)
The risk of Cancer in a Polyp is low and is found mostly in postmenopausal women. Up to 5% of Polyps that cause bleeding may be cancerous. (Lieng et al)
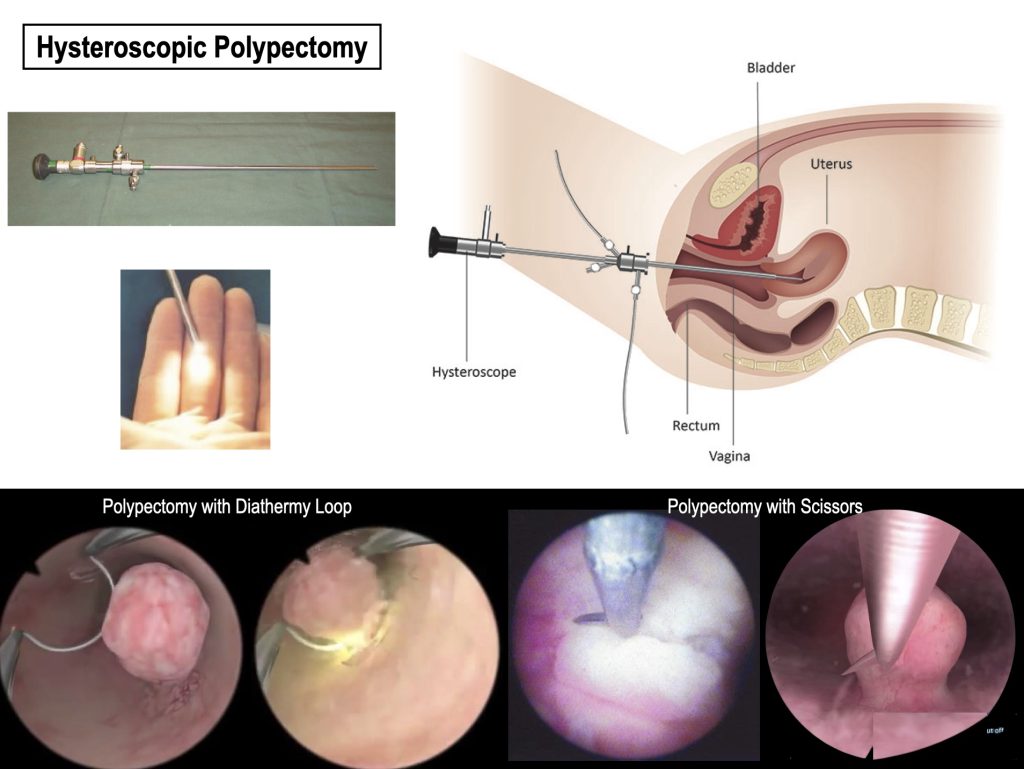
Polyps are removed by a minor surgery called Hysteroscopic Polypectomy. This surgery is done with a small scope placed inside the womb. The Polyp is visualized and removed with scissors or surgical loops.
Dilation & Curettage (D&C) without hysteroscopy is not encouraged for Polyp removal as less than 50% of Polyps are removed successfully. (Svirsky et al)