Heavy and Irregular Menstruation
Menstruation usually occurs once a month.
The normal menstruation cycle ranges from 21 days to 35 days.
Menstrual bleeding days range from 3 to 7 days and there should not be any large blood clots.
Some mild cramps may be present in the first few days.
A woman’s menstruation cycle starts around age 10 and ends at menopause around age 51.
What are the common causes?
The most common cause of heavy menstruation is Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB).
It is a condition of hormonal fluctuation leading to abnormal ovulation, heavy menstruation, and sometimes irregular cycles.
Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding is diagnosed when no other causes of abnormal menstruation are found.
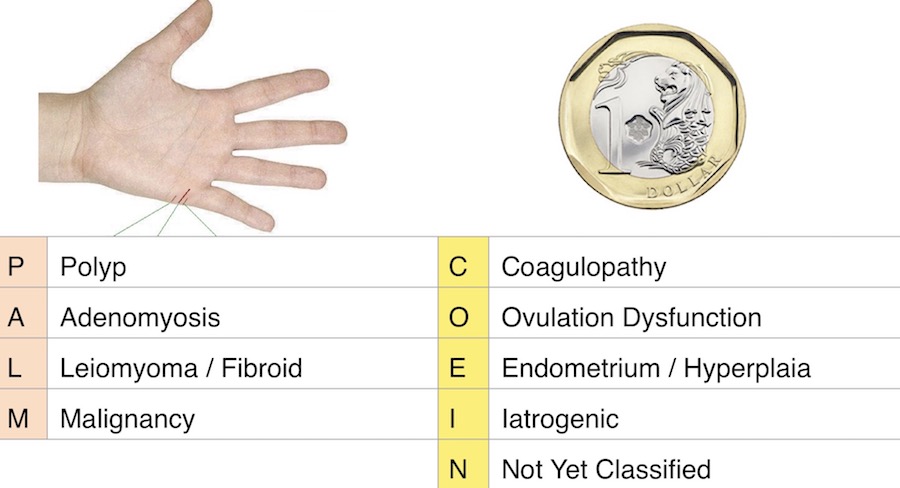
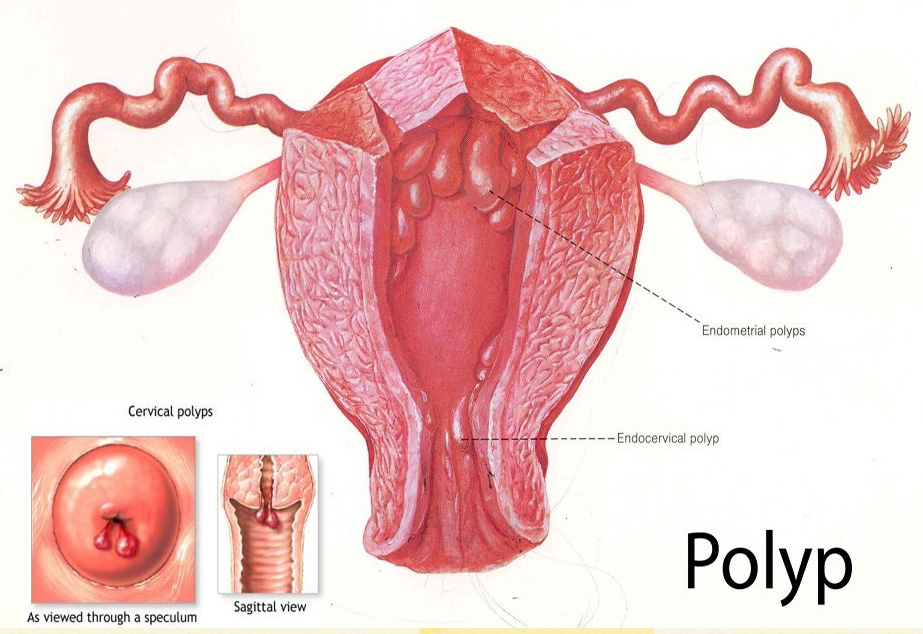
The other causes of abnormal menstruation can be listed using the PALM-COEIN classification below.
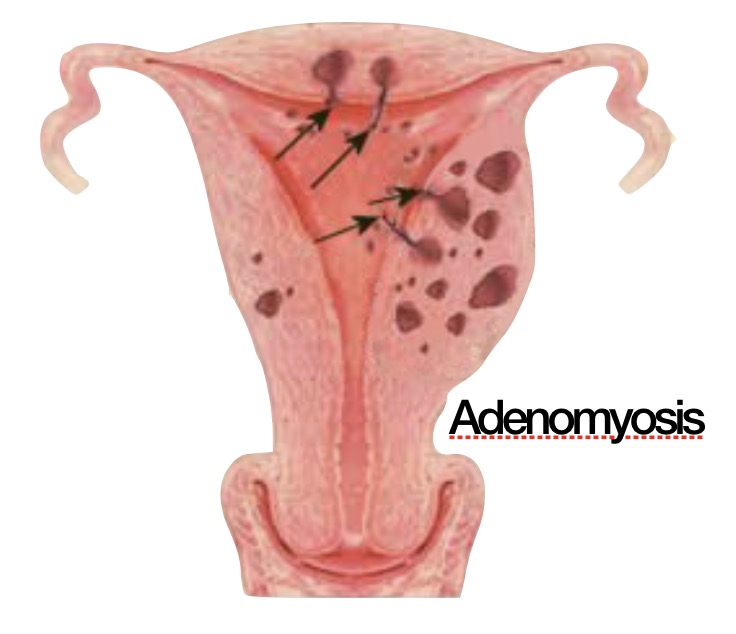
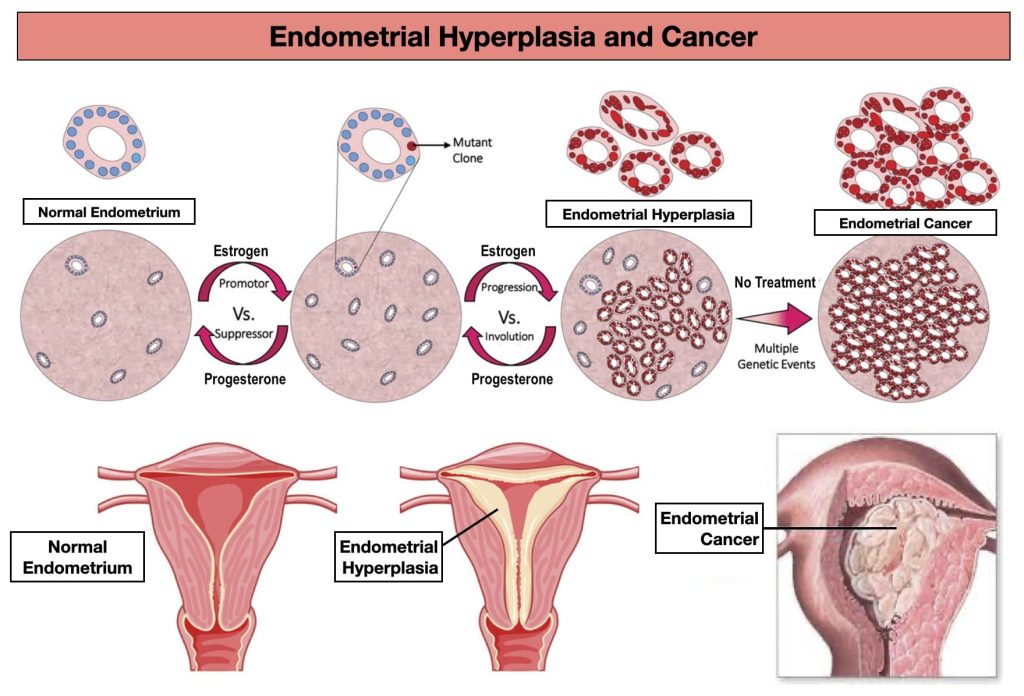
When is menstruation heavy and irregular?
Menstruation is considered abnormal when :-
❖ Bleeding exceeds a week, comes with clots, and overflows your pad
❖ Bleeding occurs every week or two without stopping
❖ Bleeding is associated with fainting spells, severe tiredness, and a drop in blood count.
❖ The Picture Bleeding Assessment Chart exceeds 100 points/day.
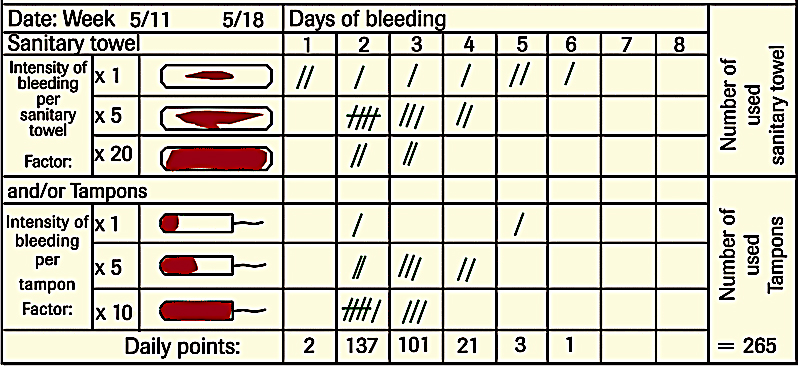
Using the Picture Bleeding Assessment Chart is a more accurate way of charting your menstruation.
Download the Picture Bleeding Assessment Chart PDF
What do I need to do?
You should see a gynaecologist if heavy or irregular menstruation persists for more than 2 months.
A detailed specialist review, physical examination, and ultrasound will usually elicit the cause.
A biopsy of the menstruation lining (endometrium) may be needed to formulate appropriate management.
A minor surgery called Hysteroscopy may be needed to look for and remove polyps/fibroids.
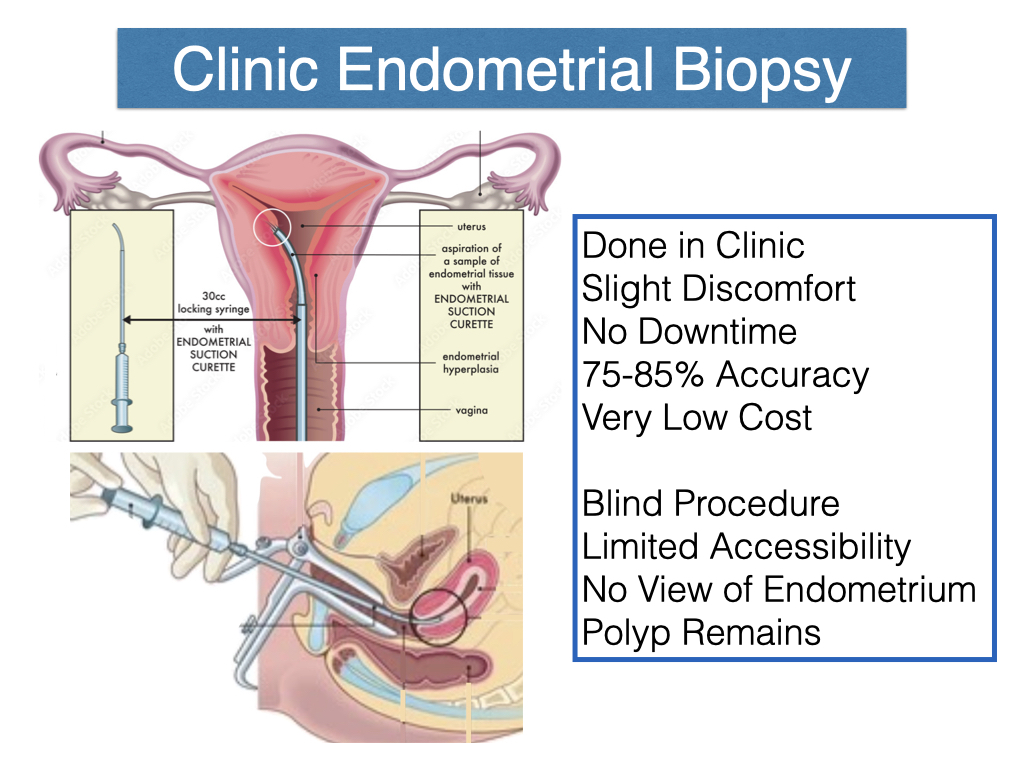
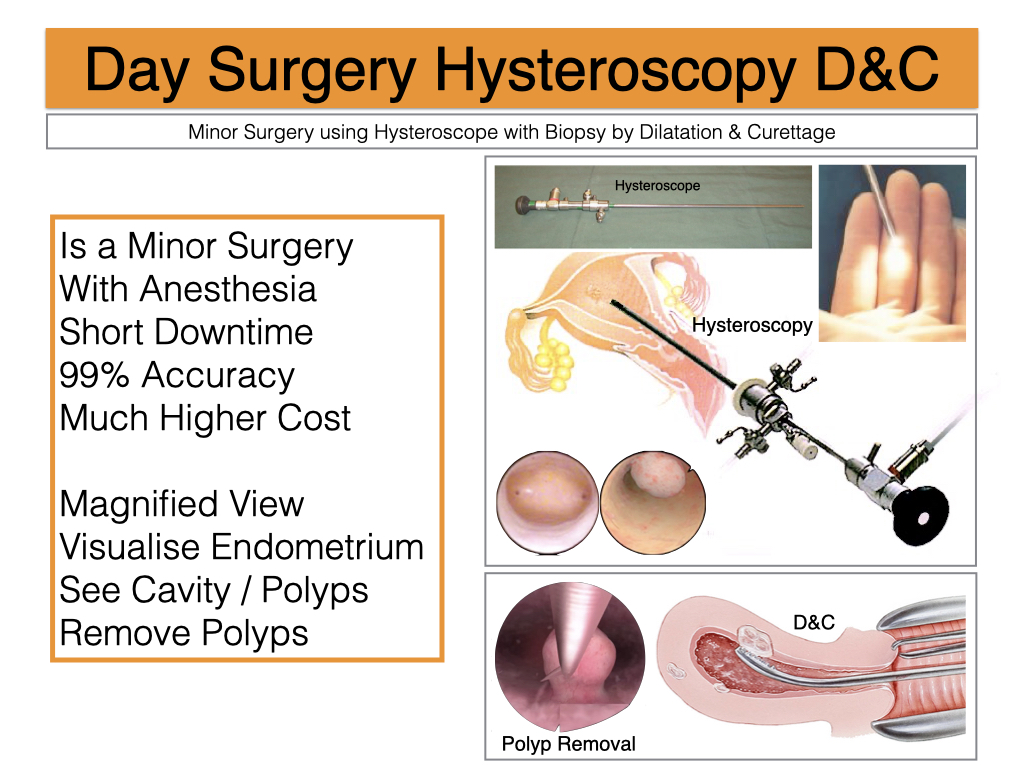
What are my treatment options?
❖ Medication both hormonal (Birth Control Pills, Menopausal GnRH Injections) or non-hormonal (Tranexemic Acid, NSAID) can reduce heavy and irregular menstruation.
❖ Mirena Intrauterine Device or Depo-Provera Injections.
❖ Hysteroscopic surgery to remove endometrial polyps or submucosal fibroids.
❖ Transcervical Resection of Endometrium. This is minor surgery to remove the menstruation lining.
❖ Major Surgery to remove the womb, preferably by Single Incision Laparoscopic Keyhole Surgery. It is done with Just One Cut of 3cm at the belly button which gives fast recovery and minimal scarring.
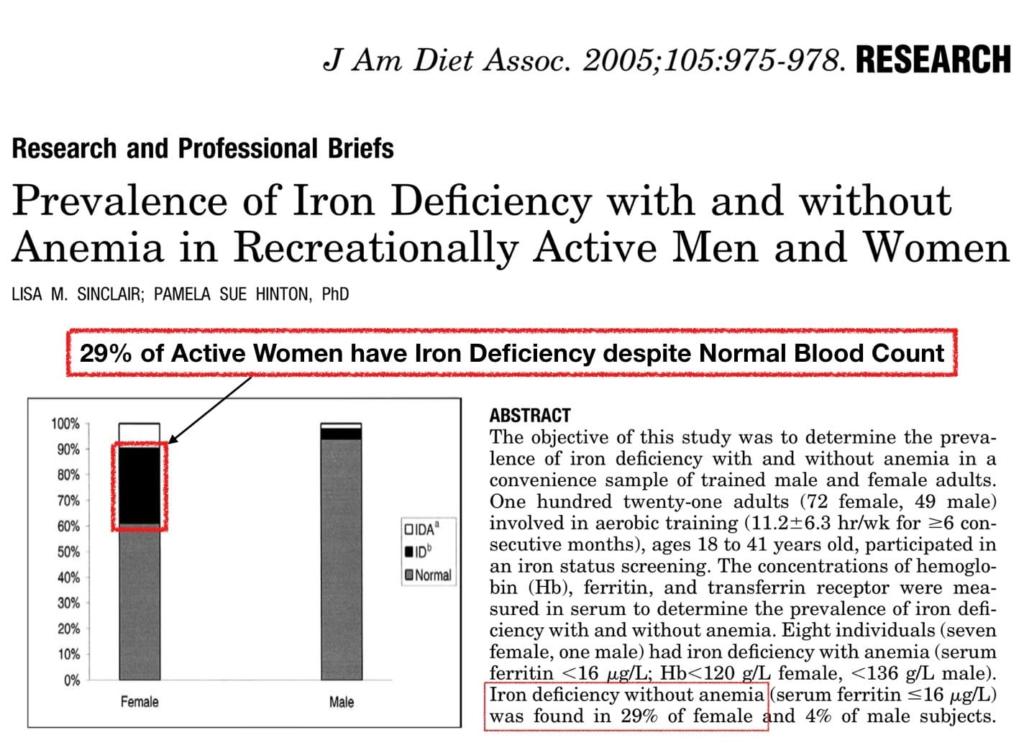
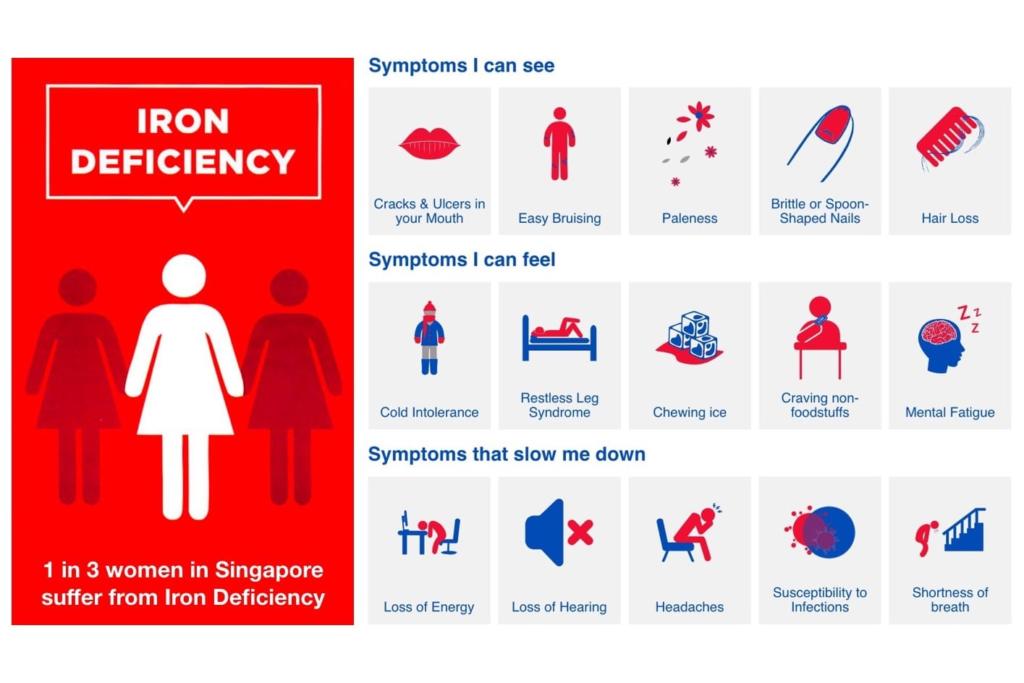
Iron Replacement Therapy
Many women with moderately heavy menstruation will have low iron stores (Ferritin) in their bodies, despite having a normal blood hemoglobin count.
It is important to take 50-100mg of elemental iron a day to prevent Iron Deficiency.