Birth Control Contraception Options
Download this booklet for more information on birth control / contraception
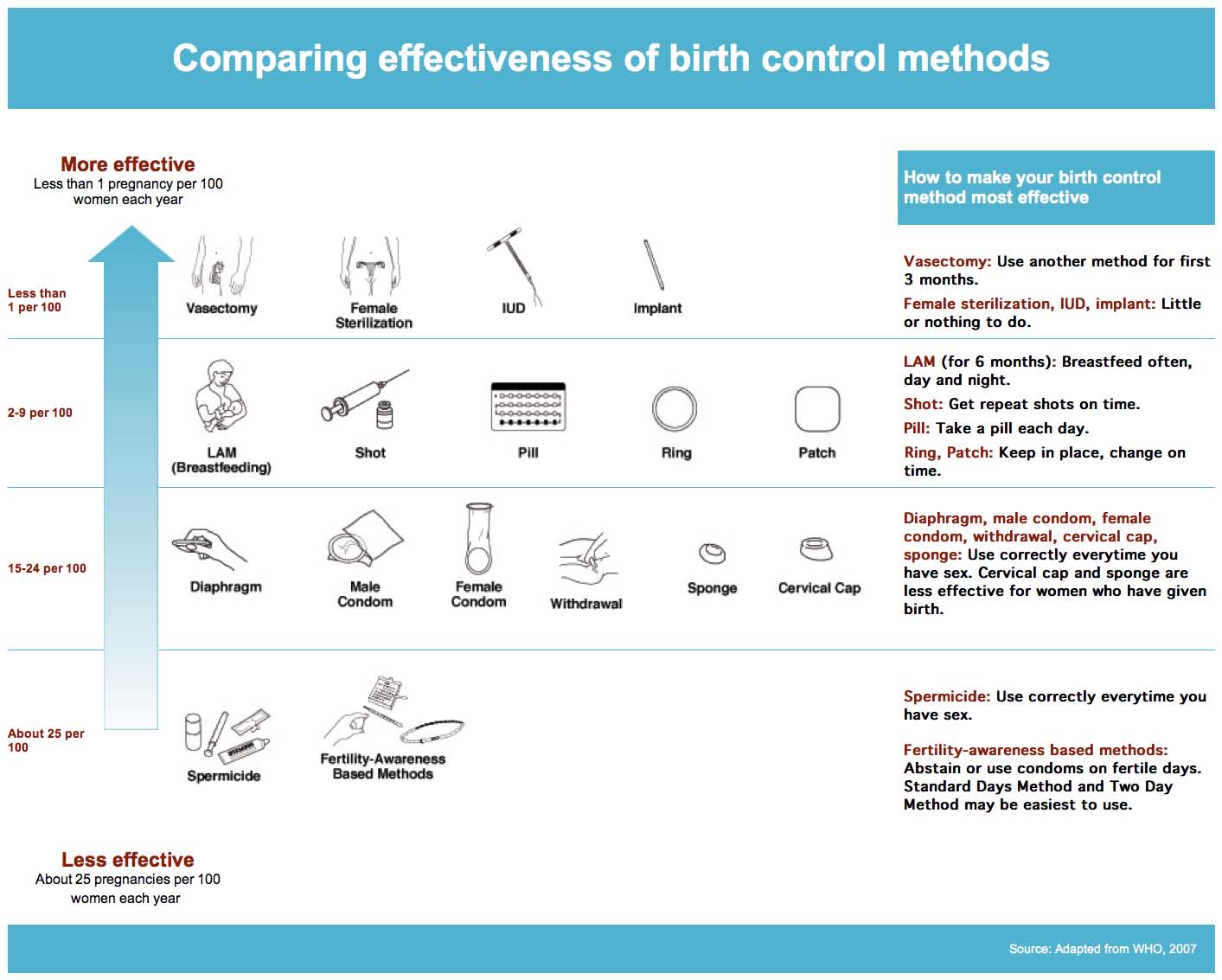
How does pregnancy happen?
In a woman, an egg is released from one of her two ovaries each month. This is called ovulation and it usually happens two weeks after her menstruation. The egg is picked up by the fallopian tube and travels within it towards the womb. Meanwhile, in the womb, the lining called endometrium thickens in preparation to receive the fertilised egg.
During sexual intercourse, the man deposits sperms in the vagina. The sperms swims up the womb into the fallopian tubes. When one sperm meets the egg in the fallopian tube, fertilisation occurs.
The fertilised egg, called the embryo then travels into the womb and implants into the womb lining (endometrium). The woman is now pregnant.
If the released egg is not fertilised, it disintegrates within 1-2 days. The thickened womb lining is then shed and bleeding occurs. This bleeding is called menstruation and it marks the start of the next menstrual cycle.
The chance of getting pregnant with unprotected intercourse is 20-30%.
To prevent pregnancy, various methods are available to prevent :-
- the egg from releasing
- the sperm from fertilising the egg
- the fertilised egg from implanting in the womb.